Data Provider
Overview
A data provider is the place where a refine app communicates with an API. Data providers also act as adapters for refine making it possible to consume different API's and data services conveniently. A data provider makes HTTP requests and returns response data back using predefined methods.
A data provider must include following methods:
const dataProvider = {
create: ({ resource, variables, metaData }) => Promise,
createMany: ({ resource, variables, metaData }) => Promise,
deleteOne: ({ resource, id, variables, metaData }) => Promise,
deleteMany: ({ resource, ids, variables, metaData }) => Promise,
getList: ({
resource,
pagination,
hasPagination,
sort,
filters,
metaData,
}) => Promise,
getMany: ({ resource, ids, metaData }) => Promise,
getOne: ({ resource, id, metaData }) => Promise,
update: ({ resource, id, variables, metaData }) => Promise,
updateMany: ({ resource, ids, variables, metaData }) => Promise,
custom: ({
url,
method,
sort,
filters,
payload,
query,
headers,
metaData,
}) => Promise,
getApiUrl: () => "",
};
refine includes many out-of-the-box data providers to use in your projects like
- Simple REST API
- GraphQL
- NestJS CRUD
- Airtable
- Strapi - Strapi v4
- Strapi GraphQL
- Supabase
- Hasura
- Nhost
- Appwrite
- Medusa
- Altogic
Community ❤️
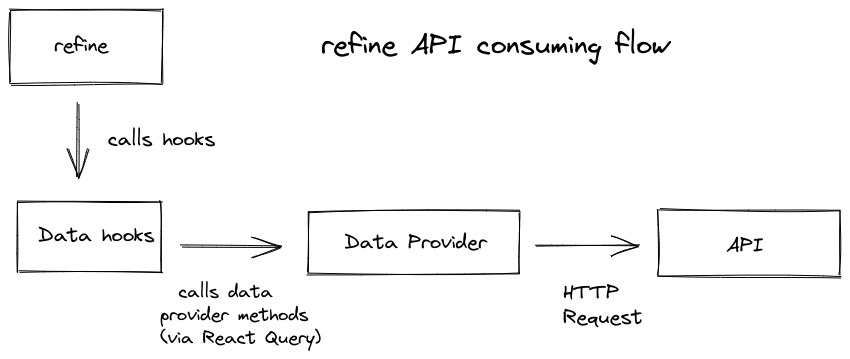
refine consumes these methods using data hooks.
Data hooks are used to operate CRUD actions like creating a new record, listing a resource or deleting a record, etc.
Data hooks use React Query to manage data fetching. React Query handles important concerns like caching, invalidation, loading states, etc.
Usage
To activate data provider in refine, we have to pass the dataProvider to the <Refine /> component.
import { Refine } from "@pankod/refine-core";
import dataProvider from "./dataProvider";
const App: React.FC = () => {
return <Refine dataProvider={dataProvider} />;
};
To activate multiple data provider in refine, we have to pass the default key with dataProvider for default data provider and we can pass other data provider with any key to the <Refine /> component.
import { Refine } from "@pankod/refine-core";
import defaultDataProvider from "./dataProvider";
import exampleDataProvider from "./dataProvider";
const App: React.FC = () => {
return (
<Refine
dataProvider={{
default: defaultDataProvider,
example: exampleDataProvider,
}}
/>
);
};
Using Multiple Data Providers
refine gives you the ability to use multiple data providers in your app. All you need to do is to pass key, value pairs to the dataProvider prop of the <Refine /> component in a form of value being the data provider and the key being the name of the data provider.
default key is required for the default data provider and it will be used as the default data provider.
const App = () => {
return (
<Refine
dataProvider={{
default: defaultDataProvider,
example: exampleDataProvider,
}}
/>
);
};
You can pick data providers in two ways:
Using dataProviderName prop in the data hooks and all data related components/functions.
const { tableProps } = useTable<IPost>({
dataProviderName: "example",
});
Using options.dataProviderName property in your resource config
This will be the default data provider for the specified resource but you can still override it in the data hooks and components.
const App = () => {
return (
<Refine
dataProvider={{
default: defaultDataProvider,
example: exampleDataProvider,
}}
/>
);
};
Example usage of multiple data providers
Creating a data provider
We will build "Simple REST Dataprovider" of @pankod/refine-simple-rest from scratch to show the logic of how data provider methods interact with the API.
We will provide you a fully working, fake REST API located at https://api.fake-rest.refine.dev. You may take a look at available resources and routes of the API before proceeding to the next step. Our "Simple REST Dataprovider" will be consuming this fake REST API.
Fake REST API is based on JSON Server Project. Simple REST Dataprovider is fully compatible with the REST rules and methods of the JSON Server.
Let's build a method that returns our data provider:
import axios, { AxiosInstance } from "axios";
import { DataProvider } from "./interfaces/dataProvider.ts";
const axiosInstance = axios.create();
const SimpleRestDataProvider = (
apiUrl: string,
httpClient: AxiosInstance = axiosInstance,
): DataProvider => ({
create: ({ resource, variables, metaData }) => Promise,
createMany?: ({ resource, variables, metaData }) => Promise,
deleteOne: ({ resource, id, variables, metaData }) => Promise,
deleteMany?: ({ resource, ids, variables, metaData }) => Promise,
getList: ({ resource, pagination, sort, filters, metaData }) => Promise,
getMany?: ({ resource, ids, metaData }) => Promise,
getOne: ({ resource, id, metaData }) => Promise,
update: ({ resource, id, variables, metaData }) => Promise,
updateMany?: ({ resource, ids, variables, metaData }) => Promise,
custom: ({
url,
method,
sort,
filters,
payload,
query,
headers,
metaData,
}) => Promise,
getApiUrl: () => "",
});
It will take the API URL as a parameter and an optional HTTP client. We will use axios as the default HTTP client.
`getMany`, `createMany`, `updateMany` and `deleteMany` properties are optional. If you don't implement them, Refine will use `getOne`, `create`, `update` and `deleteOne` methods to handle multiple requests. If your API supports these methods, you can implement them to improve performance.
create
This method allows us to create a single item in a resource.
const SimpleRestDataProvider = (
apiUrl: string,
httpClient: AxiosInstance = axiosInstance,
): DataProvider => ({
...
create: async ({ resource, variables }) => {
const url = `${apiUrl}/${resource}`;
const { data } = await httpClient.post(url, variables);
return {
data,
};
},
...
})
Parameter Types
| Name | Type | Default |
|---|---|---|
| resource | string | |
| variables | TVariables | {} |
TVariablesis a user defined type which can be passed touseCreateto typevariables
refine will consume this create method using the useCreate data hook.
import { useCreate } from "@pankod/refine-core";
const { mutate } = useCreate();
mutate({
resource: "categories",
values: {
title: "New Category",
},
});
Refer to the useCreate documentation for more information. →
createMany
This method allows us to create multiple items in a resource. Implementation of this method is optional. If you don't implement it, refine will use create method to handle multiple requests.
const SimpleRestDataProvider = (
apiUrl: string,
httpClient: AxiosInstance = axiosInstance,
): DataProvider => ({
...
createMany: async ({ resource, variables }) => {
const response = await httpClient.post(
`${apiUrl}/${resource}/bulk`,
{ values: variables },
);
return response;
},
...
})
Parameter Types
| Name | Type | Default |
|---|---|---|
| resource | string | |
| variables | TVariables[] | {} |
TVariablesis a user defined type which can be passed touseCreateManyto typevariables
refine will consume this createMany method using the useCreateMany data hook.
import { useCreateMany } from "@pankod/refine-core";
const { mutate } = useCreateMany();
mutate({
resource: "categories",
values: [
{
title: "New Category",
},
{
title: "Another New Category",
},
],
});
Refer to the useCreateMany documentation for more information. →
deleteOne
This method allows us to delete an item in a resource.
const SimpleRestDataProvider = (
apiUrl: string,
httpClient: AxiosInstance = axiosInstance,
): DataProvider => ({
...
deleteOne: async ({ resource, id }) => {
const url = `${apiUrl}/${resource}/${id}`;
const { data } = await httpClient.delete(url);
return {
data,
};
},
...
})
Parameter Types
| Name | Type | Default |
|---|---|---|
| resource | string | |
| id | BaseKey | |
| variables | TVariables[] | {} |
TVariablesis a user defined type which can be passed touseDeleteto typevariables
refine will consume this deleteOne method using the useDelete data hook.
import { useDelete } from "@pankod/refine-core";
const { mutate } = useDelete();
mutate({ resource: "categories", id: "2" });
Refer to the useDelete documentation for more information. →
deleteMany
This method allows us to delete multiple items in a resource. Implementation of this method is optional. If you don't implement it, refine will use deleteOne method to handle multiple requests.
const SimpleRestDataProvider = (
apiUrl: string,
httpClient: AxiosInstance = axiosInstance,
): DataProvider => ({
...
deleteMany: async ({ resource, ids }) => {
const response = await httpClient.delete(
`${apiUrl}/${resource}/bulk?ids=${ids.join(",")}`,
);
return response;
},
...
})
Parameter Types
| Name | Type | Default |
|---|---|---|
| resource | string | |
| ids | BaseKey[] | |
| variables | TVariables[] | {} |
TVariablesis a user defined type which can be passed touseDeleteManyto typevariables
refine will consume this deleteMany method using the useDeleteMany data hook.
import { useDeleteMany } from "@pankod/refine-core";
const { mutate } = useDeleteMany();
mutate({
resource: "categories",
ids: ["2", "3"],
});
Refer to the useDeleteMany documentation for more information. →
update
This method allows us to update an item in a resource.
const SimpleRestDataProvider = (
apiUrl: string,
httpClient: AxiosInstance = axiosInstance,
): DataProvider => ({
...
update: async ({ resource, id, variables }) => {
const url = `${apiUrl}/${resource}/${id}`;
const { data } = await httpClient.patch(url, variables);
return {
data,
};
},
...
})
Parameter Types
| Name | Type | Default |
|---|---|---|
| resource | string | |
| id | BaseKey | |
| variables | TVariables | {} |
TVariablesis a user defined type which can be passed touseUpdateto typevariables
refine will consume this update method using the useUpdate data hook.
import { useUpdate } from "@pankod/refine-core";
const { mutate } = useUpdate();
mutate({
resource: "categories",
id: "2",
values: { title: "New Category Title" },
});
Refer to the useUpdate documentation for more information. →
updateMany
This method allows us to update multiple items in a resource. Implementation of this method is optional. If you don't implement it, refine will use update method to handle multiple requests.
const SimpleRestDataProvider = (
apiUrl: string,
httpClient: AxiosInstance = axiosInstance,
): DataProvider => ({
...
updateMany: async ({ resource, ids, variables }) => {
const response = await httpClient.patch(
`${apiUrl}/${resource}/bulk`,
{ ids, variables },
);
return response;
},
...
})
Parameter Types
| Name | Type | Default |
|---|---|---|
| resource | string | |
| ids | BaseKey[] | |
| variables | TVariables | {} |
TVariables is a user defined type which can be passed to
useUpdateManyto typevariables
refine will consume this updateMany method using the useUpdateMany data hook.
import { useUpdateMany } from "@pankod/refine-core";
const { mutate } = useUpdateMany();
mutate({
resource: "posts",
ids: ["1", "2"],
values: { status: "draft" },
});
Refer to the useUpdateMany documentation for more information. →
getOne
This method allows us to retrieve a single item in a resource.
const SimpleRestDataProvider = (
apiUrl: string,
httpClient: AxiosInstance = axiosInstance,
): DataProvider => ({
...
getOne: async ({ resource, id }) => {
const url = `${apiUrl}/${resource}/${id}`;
const { data } = await httpClient.get(url);
return {
data,
};
},
...
})
Parameter Types
| Name | Type | Default |
|---|---|---|
| resource | string | |
| id | BaseKey |
refine will consume this getOne method using the useOne data hook.
import { useOne } from "@pankod/refine-core";
const { data } = useOne<ICategory>({ resource: "categories", id: "1" });
getMany
This method allows us to retrieve multiple items in a resource. Implementation of this method is optional. If you don't implement it, refine will use getOne method to handle multiple requests.
import { stringify } from "query-string";
const SimpleRestDataProvider = (
apiUrl: string,
httpClient: AxiosInstance = axiosInstance,
): DataProvider => ({
...
getMany: async ({ resource, ids }) => {
const { data } = await httpClient.get(
`${apiUrl}/${resource}?${stringify({ id: ids })}`,
);
return {
data,
};
},
...
})
We are using the query-string package for stringify.
Parameter Types
| Name | Type | Default |
|---|---|---|
| resource | string | |
| ids | BaseKey[] |
refine will consume this getMany method using the useMany data hook.
import { useMany } from "@pankod/refine-core";
const { data } = useMany({ resource: "categories", ids: ["1", "2"] });
getList
This method allows us to retrieve a collection of items in a resource.
const SimpleRestDataProvider = (
apiUrl: string,
httpClient: AxiosInstance = axiosInstance,
): DataProvider => ({
getList: async ({ resource, hasPagination, pagination, filters, sort }) => {
const url = `${apiUrl}/${resource}`;
const { data, headers } = await httpClient.get(
`${url}`,
);
const total = +headers["x-total-count"];
return {
data,
total,
};
},
}
Parameter Types
| Name | Type |
|---|---|
| resource | string |
| hasPagination? | boolean (defaults to true) |
| pagination? | Pagination; |
| sort? | CrudSorting; |
| filters? | CrudFilters; |
refine will consume this getList method using the useList data hook.
import { useList } from "@pankod/refine-core";
const { data } = useList({ resource: "posts" });
Adding pagination
We will send start and end parameters to list a certain size of items.
import { stringify } from "query-string";
const SimpleRestDataProvider = (
apiUrl: string,
httpClient: AxiosInstance = axiosInstance,
): DataProvider => ({
getList: async ({ resource, hasPagination = true, pagination, filters, sort }) => {
const url = `${apiUrl}/${resource}`;
const current = pagination?.current || 1;
const pageSize = pagination?.pageSize || 10;
const query = hasPagination ? {
_start: (current - 1) * pageSize,
_end: current * pageSize,
} : {};
const { data, headers } = await httpClient.get(
`${url}?${stringify(query)}`,
);
const total = +headers["x-total-count"];
return {
data,
total,
};
},
import { useList } from "@pankod/refine-core";
const { data } = useList({
resource: "posts",
config: {
pagination: { current: 1, pageSize: 10 },
hasPagination: true, // This can be omitted since it's default to `true` in the `getList` method of our data provider.
},
});
Listing will start from page 1 showing 10 records.
Adding sorting
We'll sort records by specified order and field.
const generateSort = (sort?: CrudSorting) => {
let _sort = ["id"]; // default sorting field
let _order = ["desc"]; // default sorting
if (sort) {
_sort = [];
_order = [];
sort.map((item) => {
_sort.push(item.field);
_order.push(item.order);
});
}
return {
_sort,
_order,
};
};
const SimpleRestDataProvider = (
apiUrl: string,
httpClient: AxiosInstance = axiosInstance,
): DataProvider => ({
getList: async ({ resource, hasPagination = true, pagination, filters, sort }) => {
const url = `${apiUrl}/${resource}`;
const current = pagination?.current || 1;
const pageSize = pagination?.pageSize || 10;
const { _sort, _order } = generateSort(sort);
const query = {
...(hasPagination ? {
_start: (current - 1) * pageSize,
_end: current * pageSize,
} : {}),
_sort: _sort.join(","),
_order: _order.join(","),
};
const { data, headers } = await httpClient.get(
`${url}?${stringify(query)}`,
);
const total = +headers["x-total-count"];
return {
data,
total,
};
},
}
Since our API accepts only certain parameter formats like _sort and _order we may need to transform some of the parameters.
So we added the generateSort method to transform sort parameters.
import { useList } from "@pankod/refine-core";
const { data } = useList({
resource: "posts",
config: {
pagination: { current: 1, pageSize: 10 },
sort: [{ order: "asc", field: "title" }],
},
});
Listing starts from ascending alphabetical order on title field.
Adding filtering
Filters allow you to filter queries using refine's filter operators. It is configured via field, operator and value properties.
const generateSort = (sort?: CrudSorting) => {
let _sort = ["id"]; // default sorting field
let _order = ["desc"]; // default sorting
if (sort) {
_sort = [];
_order = [];
sort.map((item) => {
_sort.push(item.field);
_order.push(item.order);
});
}
return {
_sort,
_order,
};
};
const mapOperator = (operator: CrudOperators): string => {
switch (operator) {
case "ne":
case "gte":
case "lte":
return `_${operator}`;
case "contains":
return "_like";
}
return ""; // default "eq"
};
const generateFilter = (filters?: CrudFilters) => {
const queryFilters: { [key: string]: string } = {};
if (filters) {
filters.map(({ field, operator, value }) => {
const mappedOperator = mapOperator(operator);
queryFilters[`${field}${mappedOperator}`] = value;
});
}
return queryFilters;
};
const SimpleRestDataProvider = (
apiUrl: string,
httpClient: AxiosInstance = axiosInstance,
): DataProvider => ({
getList: async ({ resource, hasPagination = true, pagination, filters, sort }) => {
const url = `${apiUrl}/${resource}`;
const current = pagination?.current || 1;
const pageSize = pagination?.pageSize || 10;
const { _sort, _order } = generateSort(sort);
const queryFilters = generateFilter(filters);
const query = {
...(hasPagination ? {
_start: (current - 1) * pageSize,
_end: current * pageSize,
} : {}),
_sort: _sort.join(","),
_order: _order.join(","),
};
const { data, headers } = await httpClient.get(
`${url}?${stringify(query)}&${stringify(queryFilters)}`,
);
const total = +headers["x-total-count"];
return {
data,
total,
};
},
}
Since our API accepts only certain parameter formats to filter the data, we may need to transform some parameters.
So we added the generateFilter and mapOperator methods to the transform filter parameters.
Refer to the list of all filter operators →
import { useList } from "@pankod/refine-core";
const { data } = useList({
resource: "posts",
config: {
pagination: { current: 1, pageSize: 10 },
sort: [{ order: "asc", field: "title" }],
filters: [
{
field: "status",
operator: "eq",
value: "rejected",
},
],
},
});
Only lists records whose status equals to "rejected".
custom
An optional method named custom can be added to handle requests with custom parameters like URL, CRUD methods and configurations.
It's useful if you have non-standard REST API endpoints or want to make a connection with external resources.
const SimpleRestDataProvider = (
apiUrl: string,
httpClient: AxiosInstance = axiosInstance,
): DataProvider => ({
custom: async ({ url, method, filters, sort, payload, query, headers }) => {
let requestUrl = `${url}?`;
if (sort) {
const { _sort, _order } = generateSort(sort);
const sortQuery = {
_sort: _sort.join(","),
_order: _order.join(","),
};
requestUrl = `${requestUrl}&${stringify(sortQuery)}`;
}
if (filters) {
const filterQuery = generateFilter(filters);
requestUrl = `${requestUrl}&${stringify(filterQuery)}`;
}
if (query) {
requestUrl = `${requestUrl}&${stringify(query)}`;
}
if (headers) {
httpClient.defaults.headers = {
...httpClient.defaults.headers,
...headers,
};
}
let axiosResponse;
switch (method) {
case "put":
case "post":
case "patch":
axiosResponse = await httpClient[method](url, payload);
break;
case "delete":
axiosResponse = await httpClient.delete(url, {
data: payload,
});
break;
default:
axiosResponse = await httpClient.get(requestUrl);
break;
}
const { data } = axiosResponse;
return Promise.resolve({ data });
},
}
Parameter Types
| Name | Type |
|---|---|
| url | string |
| method | get, delete, head, options, post, put, patch |
| sort? | CrudSorting; |
| filters? | CrudFilters; |
| payload? | {} |
| query? | {} |
| headers? | {} |
refine will consume this custom method using the useCustom data hook.
import { useCustom } from "@pankod/refine-core";
const { data, isLoading } = useCustom({
url: `${apiURL}/posts-unique-check`,
method: "get",
config: {
query: {
title: "Foo bar",
},
},
});
Refer to the useCustom documentation for more information. →
Error Format
refine expects errors to be extended from HttpError.
Axios interceptor can be used to transform the error from response before Axios returns the response to your code. Interceptors are methods which are triggered before the main method.
...
axiosInstance.interceptors.response.use(
(response) => {
return response;
},
(error) => {
const customError: HttpError = {
...error,
message: error.response?.data?.message,
statusCode: error.response?.status,
};
return Promise.reject(customError);
},
);
...